Table of Contents
In today’s globally connected world, fighting financial crime has become a top concern. Anti-Money Laundering (AML) programs, rules, and actions are meant to stop criminals from passing off the money they got illegally as legal income. On a basic level, what is Anti-Money Laundering?
But what is Anti-Money Laundering in simple terms? It’s a systematic approach to detect, prevent, and report activities related to financial fraud and illegal income generation.
It is very important for businesses, governments, and banking institutions to know what Anti-Money Laundering compliance means. Effective AML measures protect countries by keeping finances open and stopping illegal activities like money laundering, tax evasion, and corruption.
Countries like Pakistan need to step up their AML efforts because they are being watched around the world and need to follow international rules. Following AML rules in these areas not only helps build trust with global financial networks but also keeps the economy stable and promotes long-term growth.
What is Anti-Money Laundering (AML)?
What is Anti-Money Laundering? It is a diligent exercise aimed at ensuring that financial systems are not misused in order to “clean” money acquired through illegal activities such as drug trafficking, corruption, or tax evasion.
It refers to a set of laws, regulations, and procedures designed to detect and prevent financial crimes like money laundering, wherein money gained through illegal means is passed off as legitimately acquired income.
There are serious rules and regulations that need to be followed by financial institutions, governments, and businesses in identifying, reporting, and curbing suspected activities.
This is known as AML compliance, or in other words, being compliant with the guidelines of regulations, such as Know-Your-Customer, whereby a financial institution has to conduct due diligence on the customer and look for unusual transactions, among others.
Now, the 3 stages of Anti-Money Laundering are very important, and they are as follows:
- Placement: Money laundering begins with the introduction of illicit money in the financial system, often by way of cash deposits or transfers of money.
- Layering: The money is then to be moved through complex transactions so that the source cannot be traced.
- Integration: The cleaned money is then reintroduced into the economy as legitimate income.
These stages denote the sophisticated methods used by criminals and the need for complete AML measures to inhibit them satisfactorily.
A Brief History of AML
The concept of AML has developed over decades based on the increasing sophistication of financial crimes. AML measures have a history that originated with global actions in the mid-20th century, mainly due to the rising importance of money laundering issues caused by organized crime and drug cartels.
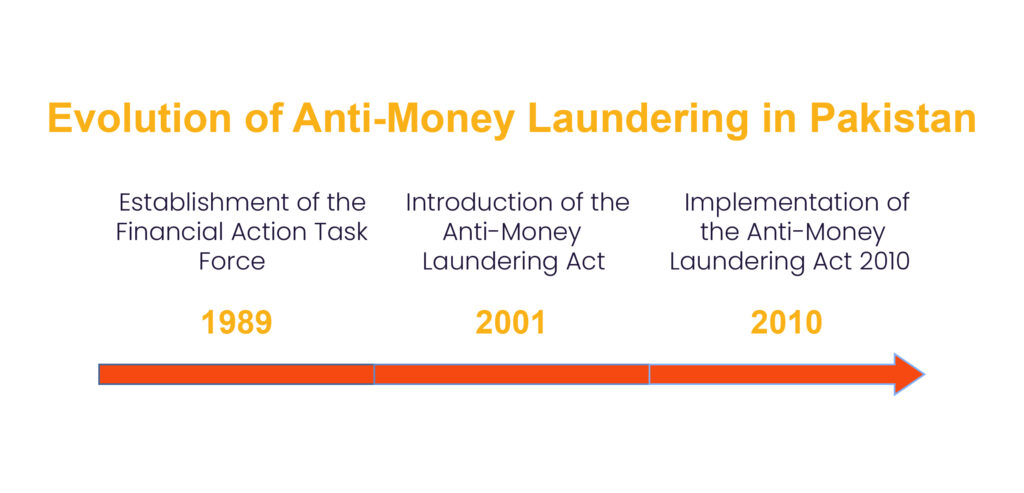
However, a turning point came when, in 1989, the Financial Action Task Force was established. It laid down overall guidelines on how to combat money laundering globally, most of which have since been adopted by countries worldwide, not least Pakistan.
In Pakistan, efforts through AML come in a structured direction by introducing specific legislation. What is the Anti-Money Laundering Act 2001? It was the first attempt by Pakistan to formalize its legal framework against money laundering.
The act defined the crime and the possible penalties and provided the framework for reporting financial institutions’ activities. However, the scope and the implementation were narrow.
- Pakistan had undertaken the Anti-Money Laundering Act 2010, introduced a broader definition of money laundering, stronger reporting mechanisms, and the establishment of the Financial Monitoring Unit (FMU) as the regulatory body in order to build a more robust framework.
- What Is Anti Anti-Money Laundering Act 2010? It has strengthened the capacity for an investigation, prosecution, and prevention of money laundering in Pakistan as it brought the country’s laws in tandem with the international standards set by the AML.
- In Pakistan, who oversees Anti-Money Laundering? AML controls and compliance issues are overseen by FMU alongside state organizations like the State Bank of Pakistan and the Securities and Exchange Commission of Pakistan.
- Their prime duties involve ensuring the implementation of AML controls within the financial institution through risk assessments and due diligence.
Why is AML Compliance Important?
Why is Anti-Money Laundering important? Anti-Money Laundering is important because AML compliance prevents criminals and terrorist organizations from misusing the global financial system.
With stringent measures in place, governments and businesses prevent bad money from entering mainstream financial institutions and save their economies and society at large.
Why is AML compliance substantial to businesses and financial institutions? Well, it ensures that the business operations are transparent and free from criminal exploitation.
Compliance helps create trust among customers, investors, and even regulators for sustained growth and reputation. It also helps institutions avoid serious legal and financial risks.
The consequences of the non-execution of a compliant AML process for businesses can be very severe. Such implications could include heavy fines, suspension of operation, loss of credibility, and criminal charges against executives.
Non-compliance could also bring about blacklisting in the international arena, thus being deprived of entering other markets.
- For example, banks and other financial institutions are subjected to greater scrutiny within international frameworks such as FATF, and not maintaining suitable AML standards is sanctioned or downgraded in risk assessments.
With an AML compliance program in place, which includes employee training and monitoring systems, one can be proactive in risk mitigation while refraining from potential legal disputes.
Who Regulates Anti-Money Laundering in Pakistan?
Who Regulates Anti-Money Laundering Pakistan? This AML regulation is overseen by a number of governing bodies, and each plays an important role in enforcing it. The FMU is considered the core of the regulatory body formed under the Anti-Money Laundering Act 2010.
Its role incorporates supervising the reporting and analysis of suspicious transactions while ensuring it adheres to both national and international standards.
The State Bank of Pakistan regulates AML compliance in the banking sector. In contrast, in the non-banking financial institutions and corporate entities, it is governed by the Securities and Exchange Commission of Pakistan.
These bodies ensure that financial institutions implement a risk-based approach, conduct due diligence, and report suspicious activities.
Anti-Money Laundering Act was enacted in Pakistan The first AML law was passed in the year 2001. However, the Anti-Money Laundering Act 2010 further strengthened the law.
The act also brought Pakistan into compliance with international standards by enhancing key aspects such as defining money laundering, penalties, and the role of reporting entities.
Acquiring an Anti-Money Laundering certificate in Pakistan is essential for individuals and companies that would like to follow the rules and regulations imposed.
In most cases, a certificate covers training from regulatory bodies or accredited institutions, teaches AML courses, and provides the skills required to prepare and carry out effective AML programs for businesses.
The 3 Stages of Money Laundering
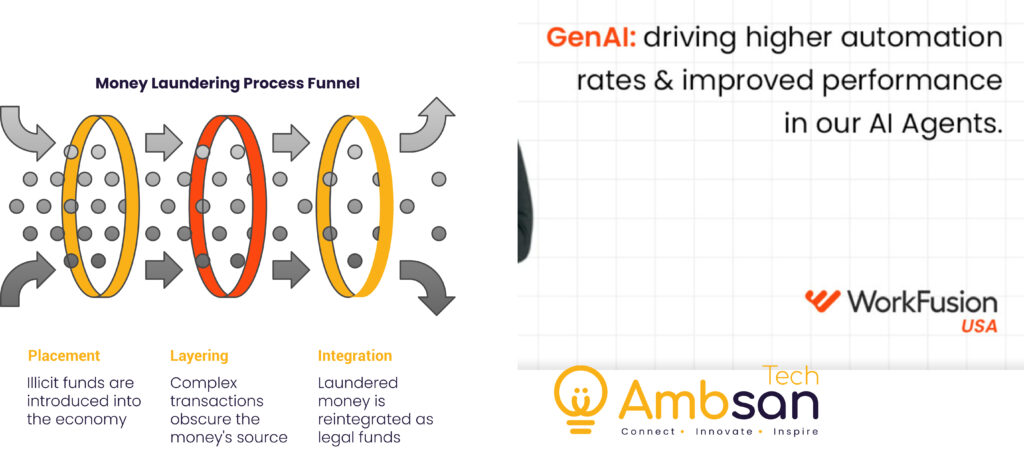
To know the three stages of anti-money laundering, it is a must to understand how criminals try to hide the illegal funds. What are the 3 phases of money laundering? These phases describe how criminal money is routed into the legal financial sector:
Placement
Here, the illicit funds collected by the criminals are laundered into the legitimate economy. It might be through placing huge lumps of cash into banks, high-value goods purchases, or money laundry through businesses with cash-intensive operations.
Layering
Layering refers to the layering of complicated financial transactions in such a way that it is impossible to identify the money’s source.
Common methods of doing this include ‘moving’ money through several accounts or by using ‘shell’ or ’empty’ entities in offshore locations or converting cash into other financial products, such as bonds or shares. It is an attempt to trace the source of funds back through layers of complexity.
Integration
In the final stage, the money laundered is injected back into the economy as appearing to be legal money.
This can appear in different forms such as investing in a business, purchasing land or other real property, or even buying other assets that seemingly make the money appear legal. Successful integration makes the crime nearly impossible to detect.
Understanding these stages will contribute significantly to a business’s establishing effective measures against money laundering.
What is AML Compliance and What Does It Involve?
Anti-money laundering compliance is essentially the procedures and policies that firms and financial institutions should follow in identifying, deterring, and reporting money laundering activities.
In this regard, compliance becomes what ensures entities have complied with national and international AML regulations to prevent the misuse of the financial system.
What Should Required Entities Do To Comply With AML Regulations?
- Customer Due Diligence (CDD): Verify the identity of clients, understand the nature of their transactions, and assess risks.
- Record-Keeping: Maintaining detailed records of financial transactions and customer information for a specified period, as mandated by law.
- Suspicious Activity Reporting (SAR): Monitoring transactions and reporting any unusual or potentially illegal activities to regulatory bodies, such as the Financial Monitoring Unit (FMU) in Pakistan.
- Risk Assessments: Regularly evaluate the risks posed by customers, products, and services to ensure compliance measures remain effective.
- Staff Training: Educating employees on AML requirements, red flags, and the importance of compliance.
How to Get an AML Certificate in Pakistan
How do you get an anti-money laundering certificate in Pakistan?
Acquiring an AML certificate involves several procedures that are ascertained with the purpose of ascertaining adherence to AML rules. How To Get Anti MoAderingring Certificate In Pakistan? Here is a step-by-step procedure for acquiring an AML certificate:
Understand Regulatory Requirements
Understand Pakistan’s main legislative framework that was brought into effect to tackle financial crimes.
Contact Certifying Bodies
Institutions like the State Bank of Pakistan (SBP) or any training provider authorized by them provide AML certification. The programs are to be used to train both the business and individuals on levels of compliance.
Comprehensive All-inclusive Courses
Apply for an AML training course to complete the basic topics like risk assessment, due diligence on customers, and the resultant reporting requirements.
Background Check
Make sure you or your organization comply with the Code of Ethics and professional and legal competencies needed to obtain the certificate. It is likely that regulatory authorities will carry out background checks as well.
Apply for Certification
You apply for certification from an issuing body that has the authority to do so. For this, typically, you would need some sort of documentation proof of training, details of the business, and evidence about the deployment of AML policies.
Maintain Compliance
You update knowledge and systems from time to time so that they are up to date with the changed AML legislation.
Who Authorizes AML-Compliant Companies And Does Background Check?
Who Can Certify Anti Money Laundering Complaint Company Background Check? Certificates are issued by the regulatory body such as SBP, SECP, or any other recognized authority in Pakistan.
These authorities also perform a detailed background verification, thus ensuring that the certificate-holding persons adhere to the standards of compliance.
AML in Banking and Cryptocurrency
AML in Banking
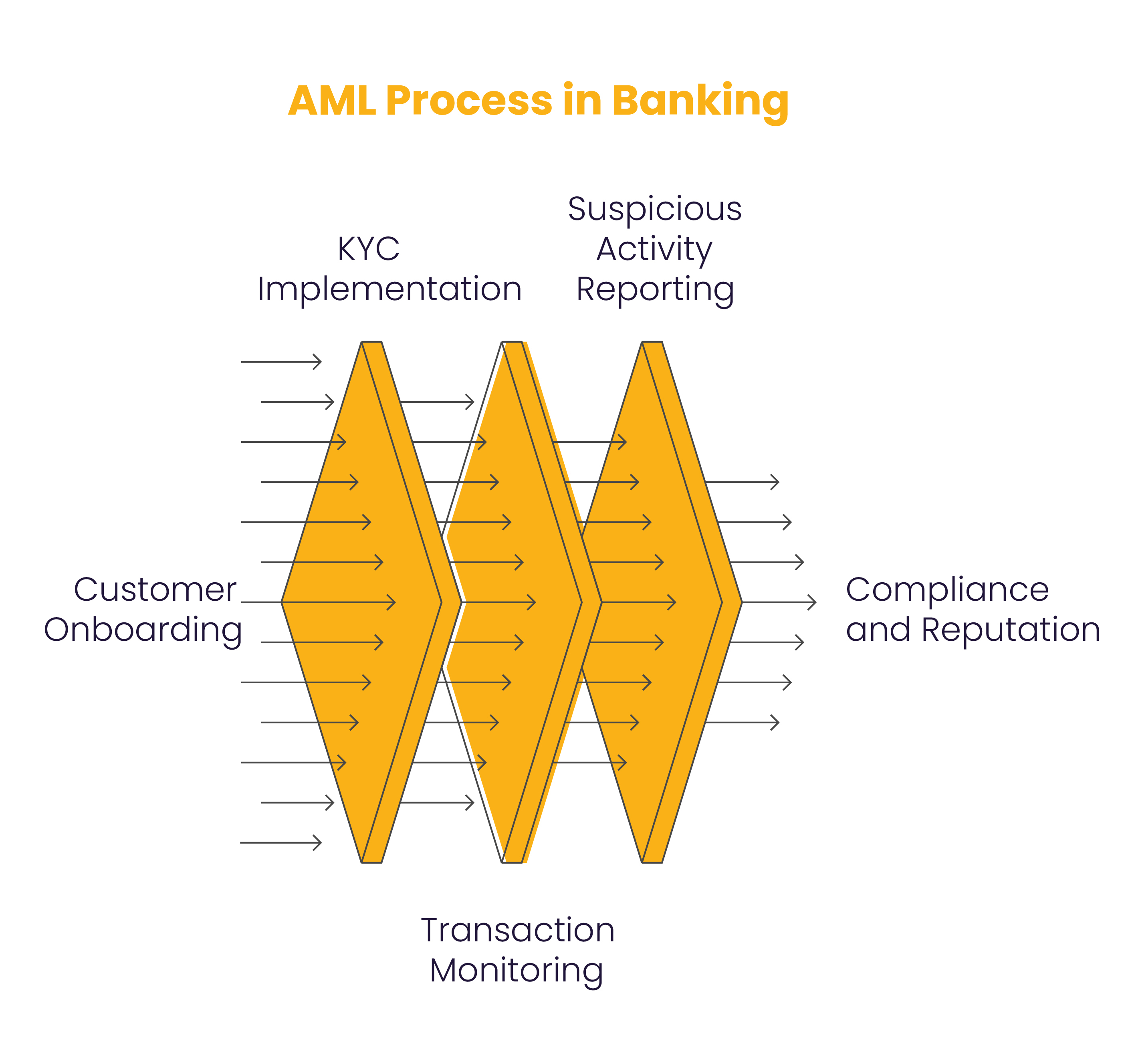
AML in banking is a basic step in the prevention of financial crime since it ensures that banks are not used to launder money or finance terrorism. This involves banks having strict Anti-Money Laundering programs that include customer due diligence, transaction monitoring, and suspicious activity reporting.
Some of the key measures banks put in place comprise:
- KYC (Know Your Customer): Identifying and Acquiring data on the customer to gauge the level of risk.
- Continuous Review: Each transaction is reviewed for unusually patterned activities.
- Report to the Regulators: Submitting SARs to the relevant authorities. For Pakistan, this will mean submitting SARs to the FMU.
Banks, therefore, will gain a reputation instead of losing it, adhere to the rules of the act, and avoid additional sanctions by observing AML regulations. Noncompliance will lead to big fines, withdrawal of licenses to continue operating, and loss of international relationships.
AML in the Cryptocurrency Industry
The increasing numbers of digital currencies have made as relevant to the cryptocurrency industry. Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum are providing anonymity and decentralized transactions, creating a lot of opportunities for money laundering.
In efforts to contain this, regulatory frameworks now require cryptocurrency exchanges and wallet providers to:
- Verify users’ identities and monitor their transactions
- Implement blockchain analytics tools that track and flag suspicious cryptocurrency transactions.
- To follow up, ensure that they adhere to the FATF standards. This means that they must follow the “Travel Rule,” where for all transfers over a particular amount, they must keep records of the transferor and the beneficiary.
- AML of banks and crypto save the financial systems from getting exploited by criminals; however, crypto changes so fast that novel legislation and compliance requirements have emerged.
AML Vs. CDD Vs. KYC: What Is The Difference?
To understand what the AML KYC process is, it is important to differentiate between AML, CDD, and KYC as these terms overlap in compliance programs.
- AML comprises all measures, laws, and procedures that prevent financial crime and are inclusive of KYC and CDD.
- KYC (Know Your Customer): A part of the AML, KYC focuses more on the identification process of the customer to confirm that they do not engage in illegal activities. The initial stage of an AML process is KYC.
- CDD (Customer Due Diligence): This is another thorough investigation of the risk profile of a customer that is done under the framework of AML. It consists of an evaluation of the patterns of transactions or business relations and also the identification of beneficial owners.
- Scope: AML covers the activities that incorporate KYC and CDD
- Reasons: The identity is confirmed during KYC while, in CDD, the risk levels and current activities are researched.
Collectively, these processes create a solid system of compliance thereby ensuring businesses are up to the minimum requirements and reduce the financial crime level to as low as possible.
AML Jobs and Certifications
Considering the multifaceted nature of monetary crimes, requirements for professionals in the AML area are on the rise. AML jobs and certifications provide attractive options in a compliance career concerning risk management.
AML Career Paths
- AML Analyst: Follows up on the transactions and focuses on suspicious activities.
- Compliance Officer: Ensures business operations adhere to AML laws and regulations.
- Fraud Investigator: Searches for cases that are likely money laundering or frauds.
- AML Consultant: Offers best practices and compliance strategies to the organizations.
- Regulatory Auditor: Evaluates and audits the institutions’ AML compliance programs.
Certifications in AML
The certifications provide a stamp of credibility and equip me with all the know-how necessary to be able to excel in AML careers. The most popular ones include
- Certified Anti-Money Laundering Specialist (CAMS): Offered by ACAMS, it is one of the most recognized AML certifications in the world.
- Certified Financial Crime Specialist (CFCS): Majorly deals with financial crime prevention that integrates AML.
- ICA AML Diplomas: These are available from the International Compliance Association, offering professional training in AML.
Certifications are also available in Pakistan. One may seek them from the State Bank of Pakistan or other recognized training providers. That knowledge of obtaining a certificate in Anti-Money Laundering within Pakistan keeps one on track toward success in local markets.
FAQS
What Is An Example Of Anti-Money Laundering?
For instance, when a bank identifies and reports strange transactions-for instance, large cash deposits with no apparent source by filing a Suspicious Activity Report (SAR) with regulatory authorities.
What Are AML Checks?
These comprise AML checks, such as checking the identity of customers, which is also known as Know Your Customer (KYC); monitoring transactions; and reporting suspicious transactions in a bid to curb financial crimes such as money laundering.
What Is Considered Anti-Money Laundering?
Anti-money laundering includes all measures, laws, and actions taken to detect, prevent, and report activities that disguise illegally obtained money as legitimate.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, AML is the need to protect the financial system’s integrity and avoid its misuse for improper activities. Understanding and compliance with AML regulations help businesses, financial institutions, and individuals make efforts toward a safer and more transparent global economy.
Implement changing AML laws like the Anti-Money Laundering Act 2010, among others, coupled with powerful compliance measures to stay on top of obligations.
Needs are not just legal obligations but steps toward trust and accountability – continuous awareness and proactive action; only in this way can there be a secure financial environment for all.
